本文翻译自: http://developer.android.com/intl/zh-cn/tools/studio/index.html
前言
除了上一篇中对Android Studio的介绍,本篇我们将继续深入了解Android Studio的功能:
- 基于
Gradle来构建应用 - 同时生成多个
apk文件(Build variants and multiple apk file generation) - 常用的代码模板以帮助你快速生成app中常见的功能模块
- 支持拖拽的布局编辑器
lint工具(帮助你性能调优,app易用性,版本兼容性以及其他一些问题)- 代码混淆(ProGuard)和app签名功能
- Google云平台的内置支持,使它易于集成Google云通讯服务和应用程序引擎
- 更多…
如果你还想知道关于Android Studio具体的使用细节,请阅读 Workflow,包括
如何在Android Studio中管理项目 和 如何在Android Studio中构建与运行项目。还有关于Android Studio最近的更新文档介绍。
项目和文件结构
Android Project view
默认情况下,Android Studio使用 Android project view来展示你的项目文件。这个视图结构是你更加易于访问到项目中的关键性文件,并且是基于Gradle构建系统的,该视图特性清单:
- 将关键性文件都展示在了一级目录下
- 将所有项目的构建文件放在公用文件夹下
- 每个项目都有清单文件夹,用来存放清单文件
- Shows resource files from all Gradle source sets
- 为资源文件分配了不同的地区,横竖屏,屏幕分辨率文件夹
1.Android project view: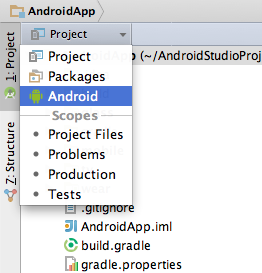
2.项目中的构建文件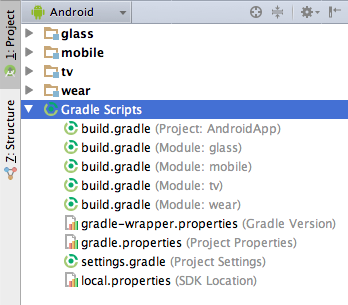
在每个project module中,都会有以下的项目结构:
java/- 存放所有的代码文件manifests/- 项目的清单文件res/- 项目的资源文件Gradle Scripts/- Gradle的构建和特性文件
比如,Android project view 在同一个文件夹下管理不同分辨率下的 ic_launcher.png 的文件。
注意: 项目在硬盘中的实际结构与 Android project view 展示的目录结构是不同的。如果你想切换至项目的实际结构,请点击 Project ,在下拉框中勾选 Project 项。
Android Studio中的其他视图结构
如果你正在使用 Project 视图结构,你应该也注意到了,不同于之前使用的 Eclipse,Andorid Studio为我们提供了不同的视图结构。每个工作空间下包含了不同的 modules, 每个 modules 中又包含了完整的项目代码,包括 src/main/ 和 src/androidTest/ 路径,资源,构建文件和清单文件。
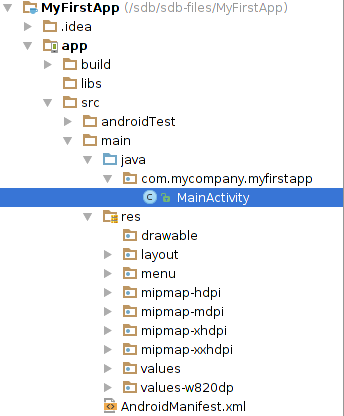
你也可以自定义文件的视图,专注于您的应用程序开发的具体方面:
- Packages
- Project Files
- Scratches
- Problems
- Production
- Tests
比如说,你选中了 Problems 视图结构,该视图就会展现项目文件中包含的任何错误,比如在布局文件中丢失的 xml 节点等。
Andorid构建系统
在Andorid Studio中,替换了 Eclipse ADT 中的 Ant 系统。它可以作为一个集成的工具从android studio菜单运行,也可以独立地从命令行。你可以使用构建系统的特性如下:
- 自定义、配置和扩展构建过程
- 将同一个项目打包成不同特性的app
- 重用代码和资源(Reuse code and resources across source sets)
android构建系统的灵活性使您可以实现这一切无需修改应用程序的源文件。关于如何在Android Studio中配置自定义的构建设置。
Debug和性能优化
Android Studio提供了一些工具来帮助你debug和提升你代码的性能,这其中包括改良的虚拟设备,内联debug, app性能分析工具。
Android虚拟设备(AVD)管理
AVD Manager能够让你在编码UI时,布局文件显示在市场大多数的设备上。你只需要在工具栏中点击 Android Virtual Device Manager,
Android Virtual Device (AVD) Manager ,创建一个新的虚拟设备,然后在模拟器中运行你的app即可。
,创建一个新的虚拟设备,然后在模拟器中运行你的app即可。
AVD Manager支持 Nexus6 和 Nexus9 设备,也支持创建自定义的设备。 Android Studio安装了 Intel x86硬件加速器,使我们的模拟器能够运行的像真机一样快。
更多信息参考 AVD Managers
内嵌的调试器
使用内嵌的调试器,以帮助你在代码的运行过程中来核查引用,表达式,变量值。具体信息如下:
- 查看运行过程中的变量值
- 引用对象
- 方法的返回值
- 运算符表达式
- Tool tip values
你只需在 Debug 窗口中,点击设置图标 ,然后勾选 Show Values In Editor 的checkbox即可.
,然后勾选 Show Values In Editor 的checkbox即可.
内存和CPU监控
Android Studio提供了内存和CPU监控器来帮助你监控app的性能,内存使用情况,cpu的使用率,查找已释放的对象,内存泄露,以及连接设备的内存情况。当你的app正在模拟器或者设备中运行,在左下角点击 Android 标签来启动运行时窗口。点击 Memory 或者 CPU 标签。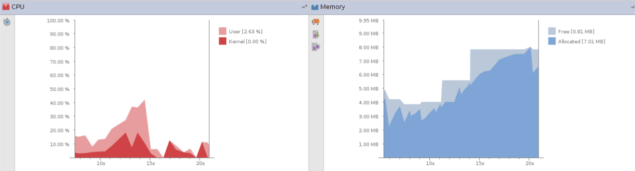
Heap(堆) dump
当你正在跟踪app的内存使用情况,同时,HPROF 视图还可以展示类,每个类中的实例和引用树来帮助你跟踪内存使用情况,查找内存泄露。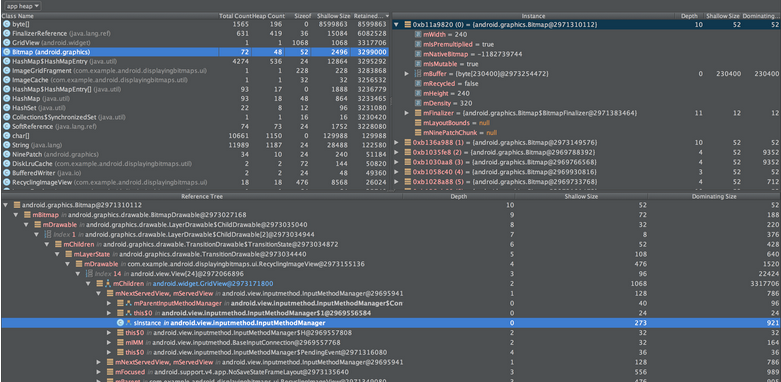
想要获取Android app堆内存的使用情况,在 Memory Monitor 中单击 Dump Java Heap 图标 。这样,AS(后面的Andorid Studio均使用缩写AS) 就会在 Captures 标签中创建一个文件名为
。这样,AS(后面的Andorid Studio均使用缩写AS) 就会在 Captures 标签中创建一个文件名为 Snapshot-yyyy.mm.dd-hh.mm.ss.hprof 堆内存的简要文件,双击这个文件来打开 HPROF 视图。
想要在AS中,转换出一个 HPROF 格式的文件,在 Caprures view 右击堆的简要文件,点击 Export to standard .hprof 即可。
内存分配跟踪
AS能够帮助你跟踪内存的分配使用情况。这样,你在app中执行某个动作的时候,就可以知道具体对象的分配细节,来帮助你调整代码结构,使你的app性能和内存使用达到最优化。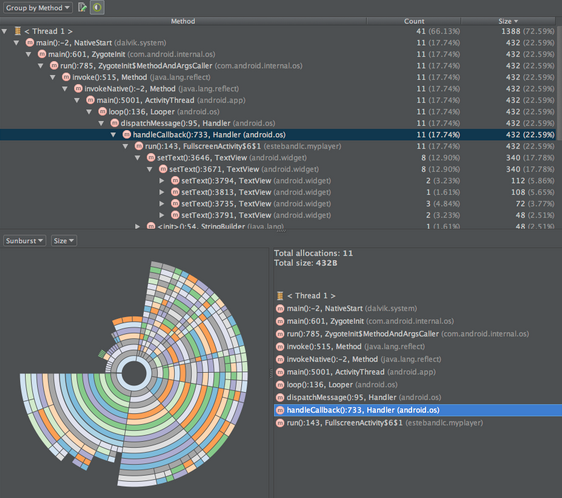
更多细节参考Memory Monitor.
数据文件访问(Data file access)
,
在Android SDK中包含了这些工具,有 Systrace,logcat, Traceview, debugging data,他们都被用来帮助我们来分析app,获取app的详细信息。
通过点击运行时窗口的左上角的 Captures来产看生成的数据文件。 在自动生成文件的列表中,双击文件来查看数据。右击任何一个 .hprof 文件来将它们转换成一个 .hprof 文件格式。
代码审查
在AS中,the configured lint and other IDE inspections run automatically whenever you compile your program. In addition to the configured lint checks, additional IntelliJ code inspections and annotation validation run to streamline code review.
Android Studio enables several lint checks to ensure:
Cipher.getInstance()is used with safe values- In custom Views, the associated declare-styleable for the custom view uses the same base name as the class name
- 安全检查片段注入
- Where ever property assignment no longer works as expected
- gradle插件版本兼容sdk
- 无误验证
- 所需的api版本
- 其他
Hovering over an inspection error displays the full issue explanation inline for easy error resolution. There is also a helpful hyperlink at the end of the error message for additional error information.
With Android Studio, you can also run lint inspections for a specific build variant, or for all build variants. You can configure the lint inspections that run by adding a lintOptions property to the Android settings in the build.gradle file.
1 | android { |
你还可以管理审核配置文件,在AS里面配置审核属性。选择 File > Setting >, 点击 Editor 选项,再点击 Inspections, 在 Inspection配置页面显示了被支持的属性值。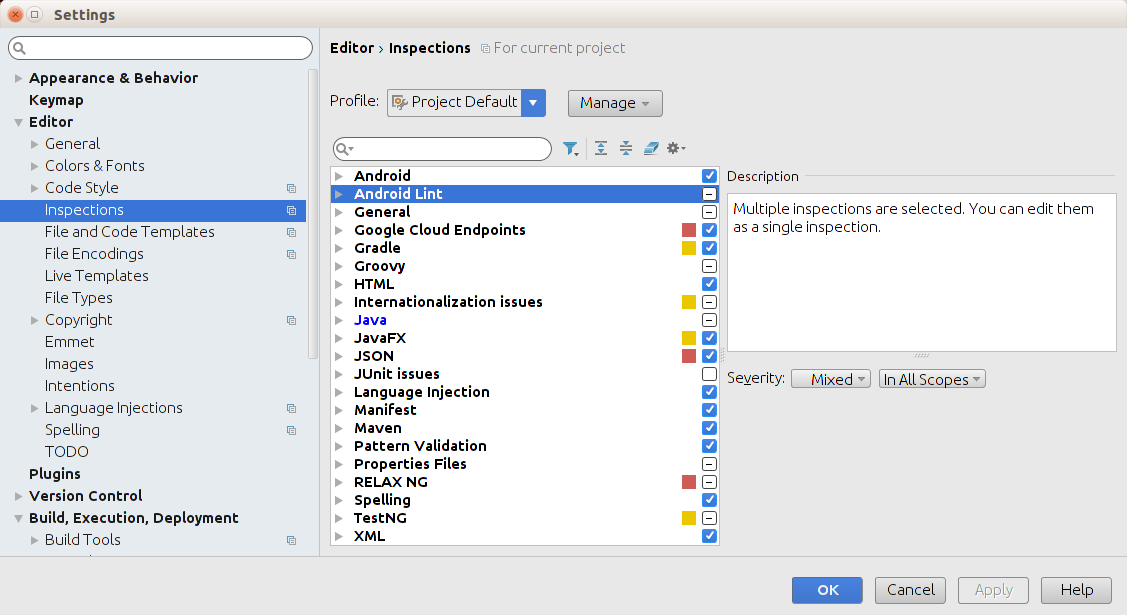
注意:要更改特定的检查通知的行为,更改检查严重性,比如从
warning级别的提示到error的级别的提示。
从命令行中运行inspections
你可以用命令行进入sdk的目录,来运行 lint inspections.
1 | sdk$ lint [flags] |
注意:
lint–show 和 –list可以被用来显示一些问题和说明。
更多信息,参考 Improving Your Code with lint和lint tool。
Annotations in Android Studio
AS支持注释变量、参数和返回值,以帮助你捕获BUG,比如空指针异常和资源类型冲突。Android SDK Manager 在Android支持库中包含了 Support-Annotations 库以供AS使用。AS在代码审查期间来验证你所配置的注释。
想在AS中为你的代码添加 annotations,首先在 Support-Annotaions 库中添加依赖:
1.选择 File > Project Structure.
2.在 Project Structure 对话框中,选择 desired module,点击 Dependencies。
3.点击 来包含一个 Library dependency.
来包含一个 Library dependency.
4.在 Library Dependency的对话框中,选择 support-annotations ,点击OK.
完成这些后, build.gradle 文件就被更新了,并已经添加了 support-annotations 的依赖。
当然,你也可以手动来完成这些工作,如下:
1 | dependencies { |
Inferring nullability
A nullability analysis scans the contracts throughout the method hierarchies in your code to detect:
- 调用可能返回null的方法
- 某个方法不应返回null
- 可能为空的变量
- 不允许为空的变量
The analysis then automatically inserts the appropriate null annotations in the detected locations.
想要在AS中使用 nullability analysis, 选择 Analyze > Infer Nullity 菜单选项。AS会在你的代码中检测到的地方插入 @Nullable 和 @NonNull 注释。在运行 null analysis 后,会验证注入的注释。
注意:在你运行了 null analysis后,nullability 分析器可能会插入 IntelliJ的
@Nullable和@NotNull注释,而不是Android的 null annotations.,如何解决这个问题呢?我们可以手动搜索这两个关键注释并全部覆盖,或者在build.gradle文件中加入com.intellij:annotations:12.0的编译依赖。参考下面的例子:
1 | dependencies { |
Validating注解
你也可以在你的代码里为各种各样的引用值手动添加 nullability,resource,枚举注解,比如 R.string ,Drawable, Color, 枚举常量。
运行 Analyze > Inspect Code来验证配置注解。
为支持注释的完整列表, either use the auto-complete feature to display the available options for the import android.support.annotation statement or view the contents of the Support-Annotations library.
更多信息参考Improving Code Inspection with Annotations。
Log信息
当你在AS上构建并运行你的app,你通过点击窗口下方的 Android 来查看 adb 和设备的日志信息。
如果你想通过 Android Debug Monitor来debug你的app,你可以点击工具栏中的 Monitor 来运行它。Debug Monitor 是一个你能够在其中找到完整功能的 DDMS,控制设备行为,等等功能的工具。他还包含了查看视图层级功能,以便帮助你优化你的布局文件。
来运行它。Debug Monitor 是一个你能够在其中找到完整功能的 DDMS,控制设备行为,等等功能的工具。他还包含了查看视图层级功能,以便帮助你优化你的布局文件。

